栈和队列¶
Java中常用的栈和队列¶
栈
// Stack , 实现如下:
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
// 方法:
// 1.pop() 弹出栈顶元素, 返回值为栈顶元素
// 2.push(int x) 将一个元素压入栈的顶部
// 3.peek() 返回栈顶元素, 但是并不移除
// 4. empty() 判断是否为空
队列
队列为 先进先出
// Queue, 实现如下: Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 方法: // 1.poll() 移除并返回队头元素 // 2.offer(int x) 在队尾添加元素(队列的入口在队尾) // 3.peek() 返回队头元素 // 4.isEmpty() 判断是否为空
Deque
Deque是双端队列(Double Ended Queue)的缩写,它允许在队列的两端进行插入和删除操作。 - 可以像栈一样在头部进行插入和删除(后进先出,LIFO) - 可以像队列一样在尾部进行插入,头部进行删除(先进先出,FIFO)

总结:
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
// 1. 实现和队列相同的效果
// add(int x) 添加元素到队列尾部
// poll() 弹出并返回队头元素
// peek() 返回队头元素
// isEmpty() 判断是否为空
// 2. 实现和栈相同的效果
// push(int x) 在队头添加元素 (相当于把元素压入栈顶 队头是出口, 相当于栈顶)
// pop() 弹出并返回栈顶(队头)元素
// peek() 返回栈顶(队头)元素
// isEmpty() 判断是否为空
// 3. 实现双端队列
// getLast() 获得队列的最后一个元素 (如果是单端的队列无法获取)
// peekLast() 获得队列的最后一个元素
// removeLast() 移除并返回队列的最后一个元素
1. 用栈实现队列¶
link : LeetCode 232
思路: 使用两个栈,一个入栈,一个出栈,当需要 pop 或 peek 元素的时候,检查出栈是否为空,如果为空将入栈的元素都弹出到出栈中, 然后出栈进行 pop 或 peek, 从而保证了元素的先进先出
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackIn;
Stack<Integer> stackOut;
public MyQueue() {
stackIn = new Stack<Integer>();
stackOut = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stackIn.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(stackOut.isEmpty()){
while(!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
return stackOut.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(stackOut.isEmpty()){
while(!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
return stackOut.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if (stackIn.isEmpty() && stackOut.isEmpty())
return true;
return false;
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
2. 用队列实现栈¶
link : LeetCode 225
思路:
方法一:使用两个队列,以队列1对核心,如果有元素进入队列,先把队列1中的元素全部放在队列2中,然后元素进入队列,再把队列2中的元素添加到队列1中
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
// 有元素进入队列,因为栈是后进先出, 因此需要将x放入队列的头部
// 先将队列1中的元素放入队列2中
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
// 将元素放入 queue1 中, 此时在队列最前方
queue1.offer(x);
// 将队列2中的元素放入队列1中
while(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
}
public int pop() {
// 弹出元素, 直接弹出队列1中的元素
return queue1.poll();
}
public int top() {
// 栈顶元素, 也是队列1中的第一个元素
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
方法二:使用一个队列实现
当有元素进入队列时, 直接入队,然后将该元素前面的元素都放在该元素的后面(从而新来的元素变成了最前面的元素,从而实现后入先出)
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
queue.offer(x);
int len = queue.size();
while(len-- > 1){
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
public int pop() {
// 弹出元素, 直接弹出队列1中的元素
return queue.poll();
}
public int top() {
// 栈顶元素, 也是队列1中的第一个元素
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
3. 有效的括号¶
link : LeetCode 20
思路: 使用栈来实现, 当遇到左括号,在栈中放入有括号,继续遍历字符串,当新的字符和栈顶字符对应(新的字符是对应的右括号),则弹出栈顶
可能遇到的情况:
- 新的字符和栈顶不一样,括号不匹配,返回 false
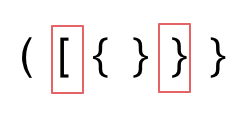 - 有新的字符,但是栈为空(说明右括号太多)
- 有新的字符,但是栈为空(说明右括号太多)
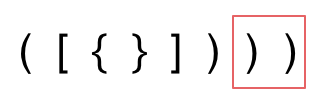 - 无新的字符,但是栈不为空(说明左括号太多)
- 无新的字符,但是栈不为空(说明左括号太多)
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char ch;
for (int i=0; i<s.length(); i++){
ch = s.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') stack.push(')');
else if(ch == '{') stack.push('}');
else if(ch == '[') stack.push(']');
// 判断是否匹配
else{
// 如果栈已经为空, 右括号太多
if (stack.isEmpty()) return false;
// 新的字符与栈顶不匹配
else if(stack.peek() != ch) return false;
else {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
// 遍历字符串结束, 判断栈是否为空
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
4. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项¶
link : LeetCode 1047
思路: 使用栈来存储遍历过的字符,当遍历新的字符时,判断新的字符和栈顶元素是否相等,如果相等,说明他们是相邻的重复项,则弹出栈顶元素;继续遍历下一个字符
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
StringBuffer resBuffer = new StringBuffer();
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char ch;
for (int i=0; i<s.length(); i++){
ch = s.charAt(i);
// 如果栈是空的, 将字符加入栈中
if (stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(ch);
continue;
}else{
// 如果栈不为空, 判断新加入的元素和栈顶元素是否相等, 如果相等则弹出
if (ch == stack.peek()) stack.pop();
else stack.push(ch);
}
}
// 弹出栈中的元素
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
resBuffer.append(stack.pop());
}
// 弹出的元素是逆序的, 因此需要反转字符串
resBuffer.reverse();
return resBuffer.toString();
}
}
5. 逆波兰表达式求值¶
link : LeetCode 150
思考: 遍历字符串,使用栈存储数字,当遇到数字时,压入栈中,当遇到运算符时,连续弹出两个数字进行运算,并把运算结果压入栈中。遍历结束,栈顶元素就是最后的结果
注意:连续弹出两个数字,第一个弹出的是 a, 第二个弹出的是 b, 如果是减法运算 则是 \(b-a\), 如果是除法运算则是 \(b/a\)
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
String temp;
for (int i=0; i<tokens.length; i++){
temp = tokens[i];
if (temp.equals("+")) {
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
stack.push(b+a);
}else if (temp.equals("-")) {
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
stack.push(b-a);
}else if (temp.equals("*")) {
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
stack.push(a*b);
}else if (temp.equals("/")) {
int a = stack.pop();
int b = stack.pop();
stack.push(b/a);
}else{
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(temp));
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
}
6.滑动窗口最大值¶
思路: 使用单调队列
因为要求出每一个滑动窗口的最大值,因此队列头存储对应的最大值
- 当窗口开始滑动,如果丢弃的值和队列头的值相等,则pop队列头
- 比较新进入窗口的值和 队列末尾的元素值,如果新进入的元素值比末尾的元素值大,则删除末尾的元素,一直到队列末尾的元素值大于等于 新加入的元素值为止
- 如果新加入的元素值比对头大,则清空原队列,将新加入的元素值作为队头
- 从而保证 队列头 存储最大值
class Solution {
class MyDeque{
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
// 添加元素
void add(int x){
// 确保添加的元素的前面的元素都大于x, 否则删除前面的元素
while(!deque.isEmpty() && x > deque.getLast()){
deque.removeLast();
}
// 把前面小于 x 的元素全部删除
// 将x添加到队尾
deque.add(x);
}
// 弹出元素
void poll(int x){
// 判断元素是否弹出
// 如果滑动窗口舍弃的元素 和队头元素相等, 则舍弃
if (!deque.isEmpty() && x == deque.peek())
// 弹出队头元素
deque.poll();
}
// 获得队头元素
int peek(){
return deque.peek();
}
}
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
// 判断数组长度是否大于1
if (nums.length == 1) return nums;
// 自定义队列
MyDeque myDeque = new MyDeque();
// 定义 resList 存储每个窗口的最大值
List<Integer> resList = new ArrayList<>();
// 先遍历第一个窗口值
for (int i=0; i<k; i++){
myDeque.add(nums[i]);
}
// 将第一个窗口的最大值(队头)添加到resList中
resList.add(myDeque.peek());
// 移动窗口
for (int i=k; i<nums.length; i++){
// 窗口移动会舍弃一个元素, 这个元素的下标是 i-k
myDeque.poll(nums[i-k]);
// 窗口移动会添加一个元素 i
myDeque.add(nums[i]);
// 将新窗口的最大值添加到 resList 中
resList.add(myDeque.peek());
}
int res[] = new int[resList.size()];
for (int i=0; i<resList.size(); i++){
res[i] = resList.get(i);
}
return res;
}
}
7. 前K个高频元素¶
堆的概念¶
"堆"通常指的是一种数据结构,用于存储和组织数据。堆通常是一个特定类型的树形数据结构,它满足堆属性。
其实 堆 就是一个二叉树,一般使用二叉树来实现堆
堆有两种主要类型:大顶堆和小顶堆。
手动实现一个堆¶
使用一维数组实现, 则当前节点下标为k, 左儿子节点为 2k,有儿子节点为 2k+1
堆的相关操作:
假设为小顶堆
- 插入一个数字
在末尾插入一个数字,并up,即如果插入的数字比父节点小, 则不断up向上, 直到大于等于父节点或者为二叉树的根节点
heap[++size]=x; up[size]; - 求集合当中的最小值
heap[1]根节点即为最小值 - 删除最小值
因为根节点是最小值,但是根节点是在数组最前面,不容易删除
因此将根节点和最后的元素交换,然后size-1,再将根节点 down
heap[1]=heap[size]; size--; down(1) - 删除任意一个元素
方法和删除最小值类似
heap[k] = heap[size], size--; down(k),up(k) - 修改任意一个元素
heap[k] = x, down(x), up(x)
前k个高频元素¶
思路: 1. 将每个元素出现的次数放入到 map 中, 其中 key 为元素值, value为出现的次数 2. 使用小根堆,遍历map,当新入堆的元素出现的次数大于 根节点的元素出现的次数, 则弹出(从而保证小根堆中保存的是出现次数前k多的元素)
class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// key: 元素值 value: 出现的次数
for (int num: nums){
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
// 使用优先级队列实现小根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((pair1, pair2)->pair1[1]-pair2[1]);
// 遍历map
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry:map.entrySet()){
// 如果小根堆中的元素小于k个, 则直接加入到小根堆中
if (pq.size() < k) pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()});
else{
// 如果新加入的元素 出现的次数比 小根堆中根节点元素出现的次数多
if (entry.getValue() > pq.peek()[1]){
// 弹出根节点
pq.poll();
pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()});
}
}
}
int res[] = new int[k];
int i=0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
res[i] = pq.poll()[0];
i++;
}
return res;
}
}